Uveitis
What is Uveitis?
Eye redness and inflammation need to be taken seriously. It could cause vision impairment, complications or loss of sight.
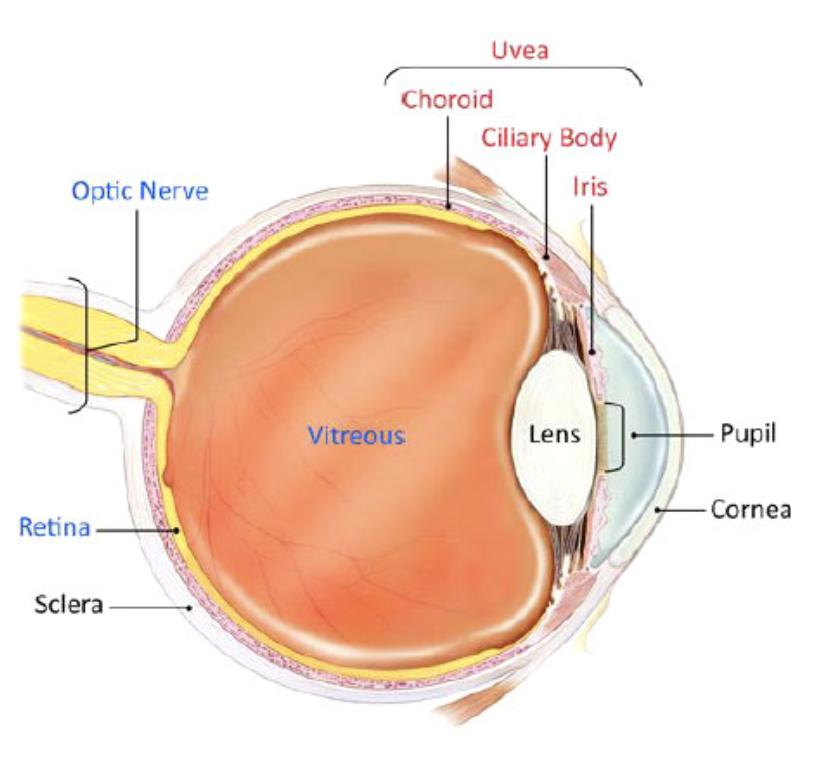
Uveitis is inflammation of the uvea, the middle layer of the eyeball. Numerous blood vessels in the uvea support and nourish the eye. Uveitis can damage vital eye tissue, leading to permanent vision loss.
There are 3 types of uveitis. They are based on which part of the uvea is affected.
- Anterior uveitis : Inflammation in front of the eye or iris
- Intermediate uveitis : Inflammation middle of the eye or ciliary body
- Posterior Uveitis : inflammation back of the eye (retina, choroid or optic nerve)
- Panuveitis : all three layers can be involved on severe case.
*The most common type of uveitis is iritis (known as anterior uveitis)
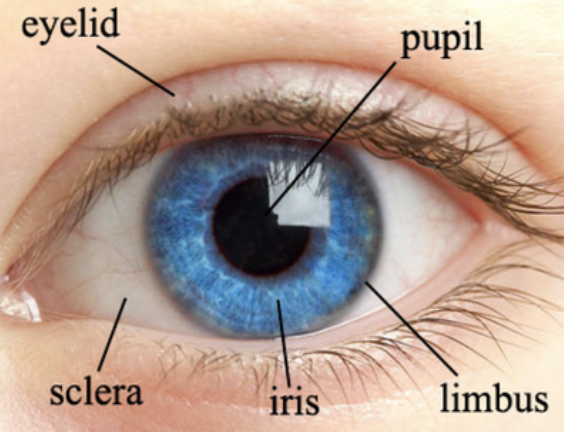
What is Iritis ?
Inflammation of the iris
Causes include infections, autoimmune disorders, or medication side effects, though often the cause is unknown.
Symptoms, which typically start suddenly, include red eye, pain, light sensitivity, blurred vision, pain during eye movement, and a small or distorted pupil. It usually affects one eye at a time and can lead to permanent vision issues if untreated.
Treatment is aimed at decreasing inflammation. Anti-inflammatory eye drops (corticosteroids) are the most common form of treatment
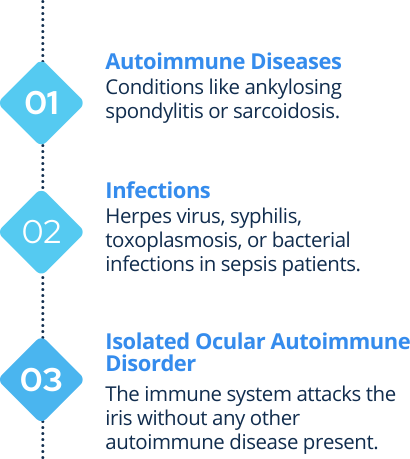
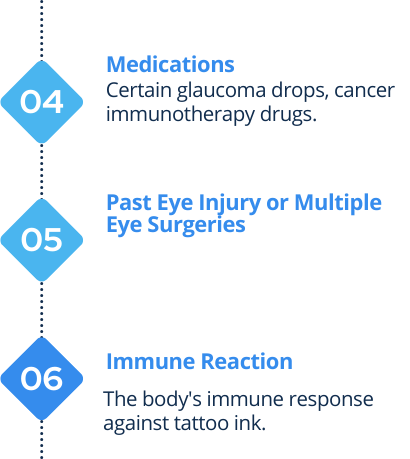
What are the Causes of Uveitis?
Uveitis is often caused by a disturbance in the body’s immune response (when the body attacks its own tissues in the eye causing harmful inflammation)

What are the symptoms?
- Red eye
- Eye pain
- Pain when exposed to bright light
- Blurred vision
- Small and/or distorted pupil
- Pain when moving the eye
- Pain when focusing on near objects (e.g, reading text or phone)

How is Uveitis Treated?
The treatment is directly dependent upon the exact areas affected in the eye and the cause is known.
Corticosteroids
- Most common treatment to reduce inflammation.
- Eye drops for anterior uveitis.
- Local injections or oral corticosteroids for posterior uveitis.
- Some cases may require additional immunosuppressive medications.
Cycloplegic Medication
- Eye drops that dilate the pupil to prevent iris sticking to the lens.
- Helps reduce the risk of scarring and pain.
Treatment of Underlying Condition
If uveitis is related to another disease or infection, that condition needs to be treated as well.
Monitoring
Regular follow-up with an ophthalmologist to minimize complications.
Treatment duration can vary, typically 6-10 weeks for anterior uveitis, while intermediate and posterior uveitis may take months or years.
Take the first step towards better eye health today!
Book your appointment now !
Your Trusted Eye Specialist Centre.

